BUS Arbitration in Computer Organization
Bus Arbitration refers to the process by which the current bus master accesses and then leaves the control of the bus and passes it to another bus requesting processor unit. The controller that has access to a bus at an instance is known as a Bus master.
Methods of Centralized BUS Arbitration:
There are three bus arbitration methods:
(i) Daisy Chaining method: It is a simple and cheaper method where all the bus masters use the same line for making bus requests. The bus grant signal serially propagates through each master until it encounters the first one that is requesting access to the bus. This master blocks the propagation of the bus grant signal, therefore any other requesting module will not receive the grant signal and hence cannot access the bus.
During any bus cycle, the bus master may be any device – the processor or any DMA controller unit, connected to the bus.
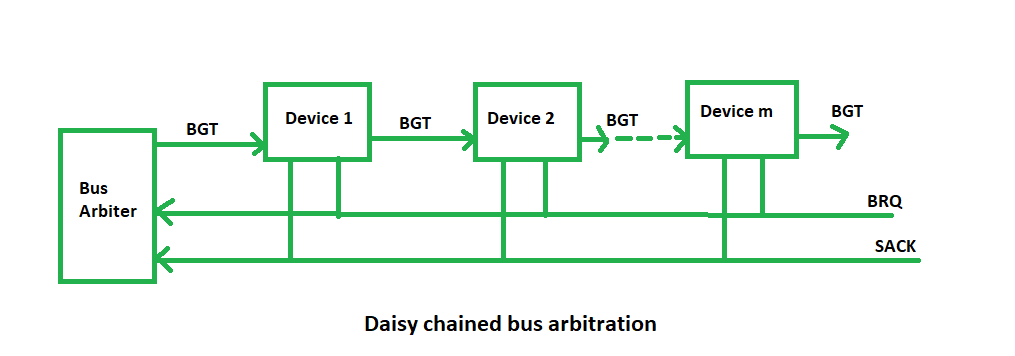
Advantages:
- Simplicity and Scalability.
- The user can add more devices anywhere along the chain, up to a certain maximum value.
Disadvantages:
- The value of priority assigned to a device depends on the position of the master bus.
- Propagation delay arises in this method.
- If one device fails then the entire system will stop working.
(ii) Polling or Rotating Priority method: In this, the controller is used to generate the address for the master(unique priority), the number of address lines required depends on the number of masters connected in the system. The controller generates a sequence of master addresses. When the requesting master recognizes its address, it activates the busy line and begins to use the bus.

Advantages –
- This method does not favor any particular device and processor.
- The method is also quite simple.
- If one device fails then the entire system will not stop working.
Disadvantages –
- Adding bus masters is difficult as increases the number of address lines of the circuit.
(iii) Fixed priority or Independent Request method –
In this, each master has a separate pair of bus request and bus grant lines and each pair has a priority assigned to it.
The built-in priority decoder within the controller selects the highest priority request and asserts the corresponding bus grant signal.
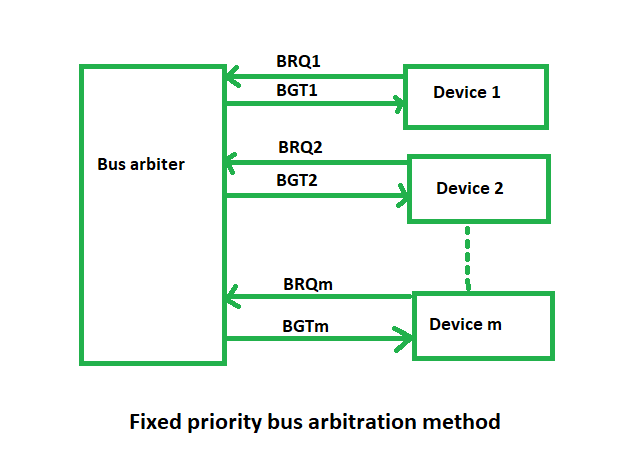
Advantages –
- This method generates a fast response.
Disadvantages –
- Hardware cost is high as a large no. of control lines is required.
Distributed BUS Arbitration :
In this, all devices participate in the selection of the next bus master. Each device on the bus is assigned a 4bit identification number. The priority of the device will be determined by the generated ID.
Uses of BUS Arbitration in Computer Organization :
Bus arbitration is a critical process in computer organization that has several uses and benefits, including:
- Efficient use of system resources: By regulating access to the bus, bus arbitration ensures that each device has fair access to system resources, preventing any single device from monopolizing the bus and causing system slowdowns or crashes.
- Minimizing data corruption: Bus arbitration helps prevent data corruption by ensuring that only one device has access to the bus at a time, which minimizes the risk of multiple devices writing to the same location in memory simultaneously.
- Support for multiple devices: Bus arbitration enables multiple devices to share a common communication pathway, which is essential for modern computer systems with multiple peripherals, such as printers, scanners, and external storage devices.
- Real-time system support: In real-time systems, bus arbitration is essential to ensure that high-priority tasks are executed quickly and efficiently. By prioritizing access to the bus, bus arbitration can ensure that critical tasks are given the resources they need to execute in a timely manner.
- Improved system stability: By preventing conflicts between devices, bus arbitration helps to improve system stability and reliability. This is especially important in mission-critical systems where downtime or data corruption could have severe consequences.
Issues of BUS Arbitration in Computer Organization :
Bus arbitration is a critical process in computer organization that has several uses and benefits, including:
- Efficient use of system resources: By regulating access to the bus, bus arbitration ensures that each device has fair access to system resources, preventing any single device from monopolizing the bus and causing system slowdowns or crashes.
- Minimizing data corruption: Bus arbitration helps prevent data corruption by ensuring that only one device has access to the bus at a time, which minimizes the risk of multiple devices writing to the same location in memory simultaneously.
- Support for multiple devices: Bus arbitration enables multiple devices to share a common communication pathway, which is essential for modern computer systems with multiple peripherals, such as printers, scanners, and external storage devices.
- Real-time system support: In real-time systems, bus arbitration is essential to ensure that high-priority tasks are executed quickly and efficiently. By prioritizing access to the bus, bus arbitration can ensure that critical tasks are given the resources they need to execute in a timely manner.
- Improved system stability: By preventing conflicts between devices, bus arbitration helps to improve system stability and reliability. This is especially important in mission-critical systems where downtime or data corruption could have severe consequences.

Comments
Post a Comment