Bus Transfer and Memory Transfer
Bus Transfer
- In a digital system of registers, a path must be provided to move information.
- Suppose separate lines are used between each register and all other registers in the system. In that case, the number of wires connecting all of the registers will be excessive because we are connecting each register with another register.
- A bus structure will not require an excessive connection. Thus it is very useful in transferring information.
- A bus is made up of a collection of common lines, one for each bit of a register, that are used to transfer binary data one by one.
There are two methods in bus transfer:
- Bus transfer using Multiplexer
- Bus transfer using Three states bus buffer
Memory Transfer
There are two memory operations in memory transfer
- Read Operation: It is the transfer of the data from memory to the outside environment.
- Write Operation: It is the transfer of the new data to be stored to the memory.
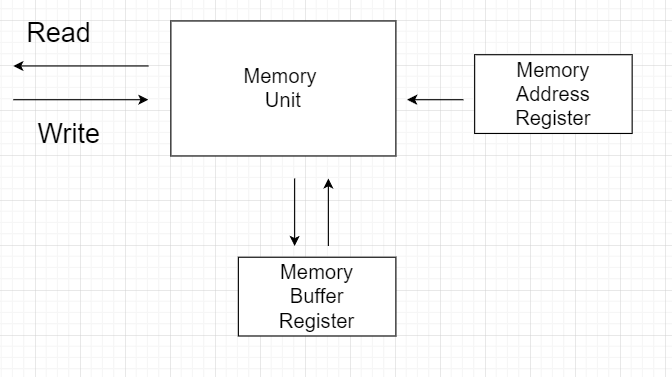
Let us have a look at some of the registers and abbreviations used for memory:
- MBR: MBR stands for memory buffer register. It is also known as (Memory Data Register) MDR. It stores the data being transferred to and from memory.
- MAR: The Memory Address Register(MAR) is the CPU register used to store the memory’s address at which the data is stored and fetched. It is often represented as AR(Address Register). M represents the memory word.
Read Operation
The transfer of data from the Address Register into the Memory Buffer Register is known as the Read Operation.
The read operation is represented by MBR ← [AR] M . It states that the Memory Unit M is transferred from [AR] representing Address register to Memory Buffer Register (MBA).
Write Operation
Write Operation is the transfer of new data into the memory.
The write operation is denoted by [AR] M ← R1. It states that the Memory M from Register R1 is transferred to Address Register([AR]).

Comments
Post a Comment